Bob K MP3 Music Files
1. Merrymeeting
Morning: Solo Flute + Harp + Strings [Musical Scene of Merrymeeting
Lake, New Durham, New Hampshire]
2. String
Quartette: Violins 1, Violins 2, Violas, + Cellos [A fragment of
the First Movement for a String Quartette]
3. Anthem to
the Mountains: Classical Organ + Strings [Musical Scene of
Merrymeeting Lake]
4. Anthem to the
Waters: Classical Organ + Strings [Musical Scene of Merrymeeting
Lake]
5. Piano Songs
Piano Song 5.1
Waltz
in F
6. Pachelbel Canon in D
Version 1
[Steinway Grand Piano]
Version 2
[Steinway Grand Piano, Hyped Accompaniment]
7. By The Greenwood Tree [Tau Tau Chapter, Sigma Chi, Washington
University of St. Louis, Spring,
1965, First Place, IFC Sing]
By The
Greenwood Tree
8. Woodwind
Quartette #1: First Movement [Oboe, English Horn, Bassoon, Contra
Bassoon]
9. Mattie's
Melody
[Ragtime Piano, for Matilda "Mattie" Berry, formerly Sister Victoria,
RIP]
10. Country Hoedown
[Fiddle, Guitar, Bull Fiddle--Country Hoedown Music!!!]
11. Rhapsody 1
[Classical, String Quartette: Violin 1, Violin 2, Viola, & Cello:
Classical Music--The First Song I composed after hearing the gorgeous
Lush Strings on my Ensoniq VFX Synthesizer]
12. Big Ballad in E
[Boston Pops-type Orchestra, Fox Trot]
13. Bob K
Theme Song [Live, Piano, Bob K Original Composition © 2006]
14. I'm
Coming Home
To You, New Hampshire [Live, Piano, Pedalbass (a set of footpedals
similar to spinet organ bass pedals, and used for playing bass notes,
for the sound of Piano plus Bass), and Vocal (no effects on the vocal
track),
Bob K Original Composition © 2002]
15. Winter Theme
[Steinway Grand Piano]
16. Prelude in F
[Symphonic Organ: To John David Antle]
17. Fugue in F
[Symphonic Organ: To John David Antle]
18. The
Smoothies' Song [Piano: Two-Beat: To Homer and Helen Hughes, The
Olde Smoothies]
19. The Merrymeeting Waltz [Piano, To Ralph and Mary Richardson]
20. Christian Hymns for Easter [Selected Hymns for Spiritual Experience during Easter.]
20.1. Beneath The Cross of Jesus [MP3 file featuring the Chapel Organ for a spiritual setting.]
20.2. Christ the Lord Is Risen Today [MP3 file featuring the Chapel Organ for a spiritual setting.]
20.3. Joyful, Joyful We Adore Thee [MP3 file featuring the Chapel Organ for a spiritual setting.]
Page Links
1. Lakeside
Studios: Music Instruction Books
2. Psychology
2.1. Operational Psychology
2.2. General Psychology
3. Philosophy
3.1. Operational Philosophy
3.2. Philosophy: Religion
4. Politics
5. Personal and
Business
Consulting
6. Physics
6.1. Operational Physics
6.2. General Physics
7. Science
8.
ProMUSE
(Professional Music/Entertainment)
9. TeachMuse (Teaching Music)
10. General Music (Music
Services, Sheet Music Services, Etc.)
11. Music Schedule 2014
Bob K MP3 Music Files
Please be advised that all files and materials are copyrighted.
Personal:
I am proud to be a member of Mensa, the Hi-IQ Society: Mensa
#100094201.
I am mighty proud to be a member of the Sigma Chi Fraternity. [Tau
Tau Chapter, Washington University, St. Louis, MO, 1965.]
1.
Lakeside
Studios: Music Instruction Books
Spiral Bound (Wirebound) Edition:
http://www.melbay.com/product-print.asp?productid=93333S
Endorsement of Deluxe Encyclopedia of Piano Chords:
http://www.jazzreview.com/bookdetails.cfm?ID=125
I am currently operating my own publishing company under the
tradename of Lakeside Studios.
I am offering a several new piano/keyboard instruction book series:
The Match & Play Music by Letter-Numbers Series, featuring
letter-numbers for all written notes for right hand melodies and left
hand accompaniment rhythm patterns.
The PB Series [Primer Book Series], for young beginners,
featuring letter-numbers for all notes.
The IB Series [Instruction Book Series], for mature beginners,
featuring reading all notes.
The QE Series [Quick and Easy Series], for impatient students,
schoolteachers, and vocalists.
Advanced piano/keyboard instruction books are under development:
PC CP [Piano Course: Country Piano]
PC LP [Piano Course: Latin Piano]
PC RB [Piano Course: Rhythm & Blues Piano]
PC RR [Piano Course: Rock & Roll Piano]
PC JP [Piano Course: Jazz Piano]
PC RP [Piano Course: Romantic Piano]
Monographs, single songs, similar to sheet music, are offered.
You can order books by PayPal or by mail.
2. Psychology
Return to Page Links
2.1.
Operational Psychology
Return to Page Links
2.1.1. Psychology:
Operational
Psychology [A Theory of Psychology/Personality/Philosophy.]
Operational Psychology was created to
present operational
definitions of psychological terms including
mind,
feelings
as
sensations and
emotions,
behavior,
personality,
mental problems, and
mental health.
The concepts and
principles of Operational Psychology and the techniques for using the
concepts and principles are intended to help psychologists organize the
field of psychology and to benefit themselves and their clients in
dealing with pure psychological problems, pure mental problems,
problems without physiological (organic) components.
You can print 2.1.1 Operational Psychology, but because it is one long
file it will
print out
23 pages or more and will not print with the proper page breaks and
formatting.
PDF files for Operational Psychology are offered herein.
The pdf files are organized as
rounds—as
a series of books to be read in sequence.
When learning any subject, learning is facilitated by opportunities to
read and study the subject several times.
In the US military, there is a simple sequence by which instructors
teach new recruits: "Tell 'em once, tell 'em twice, then tell 'em
again!"
In this section of Operational Psychology, each round (book) is
intended to present the concepts and principles of Operational
Psychology [OpPsych, or OP] from the most basic to the most advanced.
There are five Rounds for Operational Psychology. Therefore, you will
be told once (Round 1), told twice (Round 2), told three
times (Round 3), told four times (Round 4), and then told five times
(Round 5)!
If you follow this sequence—Round 1 -> Round 2 -> Round 3 ->
Round 4 -> Round 5, then learning Operational Psychology ought to be
easier than jumping to Round 5 and reading Round 5 -> re-reading
Round 5 -> re-re-reading Round 5, etc.
Round 1 presents an introduction to Operational Psychology by way of a
simple experiment an introduction to you of what motivates you.
Round 1
Round 2 presents the basic OpPsych concepts and principles of
mind,
feelings,
behavior,
personality,
mental problems, and
mental health.
Round 2
Round 3 presents the basic OpPsych concepts and principles of
mind,
feelings,
behavior,
personality,
mental problems, and
mental health in greater detail.
Round 3
Round 4 presents the intermediate OpPsych concepts and principles of
mind,
feelings,
behavior,
personality,
mental problems, and
mental health.
Round 4
Round 5 presents the advanced OpPsych concepts and principles of of
mind,
feelings,
behavior,
personality,
mental problems, and
mental health.
Round 5
You most likely will realize that Operational psychology is in fact
deep and thorough and does in fact merit and therefore require
considerable studying to learn its concepts and principles before you
can effectively learn to apply them to learn what are your personal
desires, fears and priorities, how they motivate you, how they cause
your behavior, your feelings, your personality, and both your mental
health and metal problems.
2.1.2. Psychology:
Operational Psychology:
Psychopathology, Psychodiagnostics and Psychotherapeutics [The
origins of mental problems--psychopathology, the analysis of mental
problems--psychodiagnostics, and the treatment of mental
problems--psychotherapeutics--using the concepts, principles and
techniques of Operational Psychology.]
2.1.3. Psychology:
Operational
Psychology: Basic Summary [The basic concepts, principles and
techniques of Operational Psychology.]
2.1.4. Psychology:
The Five
Basic Concepts and Principles of Operational Psychology [A general
summary of the five basic concepts and principles of Operational
Psychology]
2.1.5. Psychology: The Operational
Definition of Mind [The mind is defined operationally as an
individual's personal system of desires, fears and priorities.]
2.1.6. Psychology: The Mathematics of the
Mind [The human mind functions/operates according to principles
which can be described by mathematical expressions.]
2.1.7. Psychology: The Operational
Definitions of Mind and Feelings [The mind is an individual's
personal system of desires/fears/priorities; feelings are reactions to
realizations of desires/fears/priorities; feelings are sensations
resulting from realizations of physiological/unlearned
desires/fears/priorities or emotions resulting from realizations of
psychological/learned desires/fears/priorities]
2.1.8. Psychology: Basic Psychology
[The operational definitions of the terms and phrases used in
Operational Psychology]
2.1.9. Psychology: Proof
of the Existence of Desires, Fears and Priorities [If an
individual's mind is his personal set of desires, fears and
priorities, and if feelings
are reactions to realizations of
desires, fears and priorities, then what proof, what physical
evidence, do we have or can we find that proves desires, fears
and priorities are realities, that they actually exist, instead of
merely being the subjects or content of ideas?]
2.1.10. Psychology: The Common
Creed (Of All People)
Return to Page Links
2.2.
General Psychology
Return to Page Links
2.2.1. Psychology:
Teenage Violence
[The concepts, principles and techniques of Operational Psychology can
be applied to an understanding of violence, particularly teenage
violence; Operational Psychology and other similar cognitive
psychologies should be taught in public and private schools to help
young people understand their personal psychologies and the true
essence of feelings in general and happiness in particular so they can
avoid violence and drugs/substance abuse.]
2.2.2. Psychology:
Buddhism as a
Cognitive Psychology [Pure Buddhism, stripped of its Eastern
mysticism, deals with thinking and thinking disorders and thereby
qualifies as a cognitive psychology, probably the world's first and
therefore oldest cognitive psychology.]
2.2.3. Psychology:
The Theory of
Theories [What is a theory? An hypothesis/prediction to be proved?
Or a proven description of causality? An explanation?]
2.2.4. Psychology:
The Common
Creed (Of All People)
Return to Page Links
3. Philosophy
Return to Page Links
3.1.
Operational Philosophy
Return to Page Links
3.1.1.
Philosophy:
Operational
Philosophy [A Theory
of Philosophy.]
3.1.2. Philosophy:
A Definition of
Philosophy [The Greek definition of
philosophy; the
Operational Philosophy definition of
philosophy;
personal
philosophy;
organizational philosophy.]
3.1.3. Philosophy:
Operational
Definitions
[A specification and therefore a definition of what are operational
definitions, the types of definitions needed for clear, practical, and
effective communication in philosophy, psychology, physics, and all
other forms of science, politics, religion, and other aspects of
everyday living.]
3.1.4. Philosophy:
The Source of
Causality [From Operational Philosophy.] [All chains of
causality – causes causing effects;
effects being caused by causes--lead back to the source of causality;
and the source of causality is matter/energy. The source of causality
is a necessary concept
because it is involved in the cosmological logical argument for the
existence of God.]
3.1.5. Philosophy:
The Natural
Code of Morality [A Theory of Morality. 1. All men are
born Selfish, S, seeking to achieve their desires and to maximize their
happiness; 2. They become Personally Selfish, or PS, seeking to achieve
their desires and to maximize their happiness without regard for or
consideration of the happiness of other people; 3. They learn to
become Socially Selfish, or SS, seeking to achieve their desires and to
maximize their happiness with regard for/consideration of the desires
and happiness of other people by negotiating and seeking to achieve
common desires with those other people. By this sequence of
1. S – 2. PS – 3. SS a natural morality is created, civilizations are
created, and are
reborn in every generation when individuals learn that to achieve many
if not most if not all of their desires they need the ready, willing
and able cooperation of other people for which they must be ready,
willing and able to
cooperate with those other people to negotiate and to
seek to achieve common desires.]
All men are selfish.
Man's
natural selfishness will lead him to create a natural code of
morality.
The
natural code of morality will be based upon the natural selfishness of
man and not the dogma of mystical beings.
Man
will
follow the natural code of morality for selfish reasons.
3.1.6. Philosophy:
When
Does/Did Life Begin? [A description of the fundamental facts
concerning when life begins; which shows that life began a long time
ago when life forms formed from nonlife forms; which shows that life
does not begin at conception; which shows that life is continued at
conception.]
3.1.7. Philosophy:
Do We Have Free Will?
[An essay on the concept of free will; do we have free will, or,
instead, do we have the freedom to choose?]
3.1.8. Philosophy:
The
Philosophers' Delusion [Philosophers often assert that our
perceptions are illusions and that, therefore, we cannot perceive
reality directly; this is nonsense, because for millions of year we
humans have been able to rely upon our perceptual senses of sight,
hearing, touch, smell, and taste for observing and thereby obtaining
accurate
information about the people, things and events of reality.]
3.1.9. Philosophy/Psychology:
Human Nature
[A short {five-page} summary of the philosophy of human nature. {Based
upon Operational Psychology.}]
3.1.10. Philosophy:
Natural Morality:
Standards for Judging Who Is PS/PSP and Who Is SS/SSP [Who is
PS/PSP and how do we know? Who is SS/SSP and how do we know? Standards
are needed for understanding natural morality and observing which
individuals are PS/PSP and which individuals are SS/SSP.]
31.11. Philosophy:
Why Do People Follow
Moral Codes? [Why do people follow moral codes? Why do people
follow religion-based moral codes, codes based upon belief in the
existence of gods? Why do people follow natural moral codes, codes not
based upon belief in the existence of gods? Among many reasons, one
natural reason stands out: human selfishness.]
3.1.12. Philosophy:
Logical
Fallacy: Belief in X = Knowledge of X [When belief = opinion
unsupported by enough facts, proof, as physical evidence, reliable
eyewitness reports of physical evidence, or/and logical arguments whose
premises are verified by physical evidence and/or reliable eyewitness
reports of physical evidence, then Belief in X n= Knowledge of X, where
n= is the symbol for 'is not equal to' or 'not equal to' and is used in
recognition of the fact that not all computers recognize the 'not equal
to' symbol in all computer fonts.]
3.1.13. Philosophy:
The Theory of Axioms
[An axiom is self-evident and can be proved by inductive
reasoning/logic following the form of the If (P), Then (Q) logical
argument and verifying the premise (P) by the observation of a large
sample; an axiom can also be proved by deductive reasoning/logic
following the form of
the P = Q = X logical argument and verifying the P premise
and the Q premise by observation of a large sample.]
3.1.14. Philosophy:
The True Facts
of Human Life [Human life forms evolved from early life forms to
early human life forms to human parents who produce human gametes when
when fertilized produce human zygotes.]
3.1.15. Philosophy:
What Is Proof? [Proof is
support for an assertion or a proposition or an opinion; but what,
exactly, is proof?]
3.1.16. Philosophy:
The Theory of
Theories [What is a theory? An hypothesis/prediction to be proved?
Or a proven description of causality? An explanation?]
3.1.17. Philosophy:
The Necessity for
Human Cloning and Embryonic Stem Cell Research (ESCR) [If the
proper intent is the preservation of the human race then human cloning
and ESCR is a necessity]
3.1.18. Philosophy:
Logical Arguments
[What are logical arguments?]
3.1.19. Philosophy:
What Is Logic? [
If
philosophy is the discipline which
describes the proper reasoning/thinking for the
development of accurate
concepts {mental representations/ideas
of people/objects/events},
principles {mental
representations/ideas of relationships. esp. causal relationships
between/among people/objects/events wherein people/objects/events
who/which are causes cause/create people/objects/events who/which are
effects} and
techniques {practical applications of concepts and
principles} for decision-making and problem-solving
and if
logic is necessary for useful philosophy,
then
what is logic?]
3.1.20. Philosophy:
Refutation of Zeno's
Paradox Inre Achilles and the Tortoise [What is Zeno's Paradox inre
a race between Achilles and a Tortoise? Will Achilles always run faster
than the Tortoise?]
3.1.21. Philosophy:
The Basis of
Knowledge [What is
knowledge? True/accurate
concepts
(mental representations/idea of people and/or objects) and
true/accurate
principles [mental representations of events,
causal relationships between/among people/objects], and practical
techniques
(useful applications of concepts/principles for solving problems--for
learning (1) how to achieve desires (wanting people/objects/events) and
(2) how to avoid fears (not-wanting people/objects/events). If
P/Condition(s), Then Q/Consequence(s) logical arguments provide
specifications of causality and therefore of knowledge inre causality.]
3.1.22. Philosophy:
If P, Then Q
Logical Arguments and 100% Predictability
[In an If P, then Q logical argument the P functions as a set of
Conditions, P/Conditions, and the Q functions as a Consequence (or a
set of consequences), Q/Consequences; when the P/Conditions are
precisely specified, they cause the Q/Consequences with 100%
predictability.]
3.1.23. Philosophy:
What Is Philosophy?
[What is philosophy? What is the value
of philosophy? What is the philosophy of philosophy? What do people do
when they philosophize?]
3.1.24. Philosophy:
Basic Philosophy
[The operational definitions of the terms and phrases for the basic
philosophy of Operational Philosophy]
3.1.25. Philosophy:
Common Sense
[Rhetorical Question: What is common sense? Rhetorical Answer: Common
sense is an individual’s or organization's philosophy which consists of
concepts/principles/techniques which achieve desires/avoid fears/solve
problems and enable individuals to experience happiness and to avoid
experiencing unhappiness.]
3.1.26. Philosophy:
Common Sense v
Critical Thinking [How does common sense compare to critical
thinking?]
3.1.27. Philosophy:
Mediocre Minds
[What are Great Minds V Mediocre Minds? How can mediocre minds be
identified?]
3.1.28. Philosophy:
External v
Internal Worlds [What is an external world? What is an internal
world? How can humans observe the external world v the internal world?]
3.1.29. Philosophy:
Do We Have Free Will?
[What is
free will? Do we
have free will? Or freedom to choose?]
3.1.30. Philosophy:
Abbreviations
and Acronyms for Philosophy [Philosophers interested in Operational
Philosophy could benefit from abbreviations and acronyms.]
3.1.31. Philosophy:
Distinguishing
Judgments from Feelings [The feeling which is the emotional
reaction expressed in the sentence "I feel ___ (happy/unhappy)!" is
different from the judgment expressed in the sentence "I feel that ___
(you should ___, they must ___, the world ought to be ___)!"; therefore
judgments can be, and ought to be, distinguished and thereby
differentiated from feelings.]
3.1.32. Philosophy:
How Do We
Know There Is An External World Outside/Beyond Us? [We become aware
and thereby learn of the external world by at least nine basic
reaasons.]
3.1.33. Philosophy:
If P,
Then Q Logical Arguments and Causality [If P, Then Q logical
arguments are descriptions and predictions of causality—the sequence in
which Ps which are conditions and causes cause Qs which are
consequences and effects.]
3.1.34. Philosophy:
The Common
Creed (Of All People)
3.1.35. Philosophy:
The Duck Theory
[If (P) it looks like a duck, quacks like a duck, and acts like a duck,
the (Q) it's a duck! People are more so what they do then what they
say.]
3.2.
Philosophy: Religion
Return to Page Links
3.2.1.
Philosophy: Why I Am An Agnostic
[The long version of my continuing journey inre conceptualizing reality.]
Do mystical beings exist?Therefore, the fundamental
problem for all who seek the truth
concerning religion is determining if or not mystical beings exist, or
if they are figments of imagination. This article is my story
concerning my philosophy of life. NOTE: This article is being updated
continuously. Check frequently
for updates.
3.2.2. Philosophy: Why I Am An
Agnostic [Short Version] [The short version of my continuing
journey inre conceptualizng reality.]
3.2.3. Philosophy: Standards for the
Analysis, Evaluation and Judgment of Holy Books [Without standards,
anything goes; a proposal for standards for the analysis, evaluation
and judgment of holy books.]
3.2.4. Philosophy: Contradictions in
the Christian Bible [The Christian Bible contains contradictions,
two or
more stories which differ in details, facts, including sequence errors.
Mystical beings [gods/goddesses] should inspire only the truth and thus
error-free holy works, including translations. The presence of
contradictions in a holy book are evidence that the book was not
inspired by mystical beings, and that it is therefore not a holy book. See
for yourself.]
3.2.5. Philosophy: Standards for the
Analysis, Evaluation and Judgment of Gods [Without standards,
anything goes; a proposal for standards for the analysis, evaluation
and judgment of gods.]
3.2.6. Philosophy: Disproofs of
the Existence of Gods: The Term Perfection Is Illogical
[Theoretically, until further notice, it is impossible to prove a
negative; many disproofs of the existence of gods (proofs of the
nonexistence of gods) use the term "perfection" in an illogical attempt
to disprove the existence of gods.]
3.2.7. Philosophy: A Rational Concept
of Gods [The omni-everything concept of gods
{omnipotent/all-powerful/can do anything, omniscient/all-knowing/knows
everything, and omnibenevolent/all-caring/all-good} has a logical
contradiction: If Evil exists as a
being or as a force, then the omni-everything god is
(A) not omnipotent, because it cannot control Evil,
(B) not omniscient, because it does not know Evil exists, or that Evil
would exist, or/and (C) not omnibenevolent, because it would not care
enough about mankind to prevent
Evil to exist or to harm mankind; thus the omni-everything concept of
gods is illogical/irrational; but a non-omni-everything concept of gods
might not be illogical/irrational, and, instead, might actually be
logical/rational.]
3.2.8. Philosophy: Definitions
of Theist/Theism, Atheist/Atheism, and Agnostic/Agnosticism
[If theists cannot prove gods exist/theism is true, and if atheists
cannot prove gods do not exist/atheism is true, then the only rational
philosophical position to hold concerning religion is agnosticism.]
3.2.9. Philosophy: Definitions
of Theist/Theism, Atheist/Atheism, and Agnostic/Agnosticism
(Longer Version) [The longer version of 3.2.8.]
3.2.10. Philosophy: The Bel (Baal)
Myth Parallels to the Jesus Myth [The Assyrian/Babylonian myth of
the death and resurrection of the god Bel (Baal, or Bel-Marduk, or
Marduk-Bel) offer mythical elements which parallel the mythical
elements of the birth of Jesus in the Jesus myth.]
3.2.11. Philosophy: The Judeo-Christian,
Chaldean and Hindu Flood Myth Parallels [The presence of similar
flood myths in the Chaldean and Hindu cultures suggests that the
Judeo-Christian flood myth is a plagiarization of earlier flood myths.]
3.2.12. Philosophy: The Hindu
Krishna and Christian Jesus Myth Parallels [The older Hindu Krishna
myth from 1200 B.C. might have been the source of elements of
the Christian Jesus myth.]
3.2.13. Philosophy: What Is Proof? [Proof is
support for an assertion or a proposition or an opinion; but what,
exactly, is proof?]
3.2.14. Philosophy: Biblical Fictions
[A fiction is a false account of people/things/events; the Christian
Bible contains fictions
in which Old Testament prophecies are supposed to be predictions of New
Testament people/things/events; supposedly the Xn OT prophecies prove
the NT is true and the NT fulfillments of OT prophecies supposedly
prove
the OT is true; Xn OT prophecies are local for place and immediate or
nearby for time and not of NT people/things/events seven hundred years
later than the prophecies.]
3.2.15. Philosophy: The
Egyptian Horus Myth Parallels to the Jesus Myth [The Egyptian myth
of the birth of the god Horus offer mythical elements which parallel
the mythical elements of the birth of Jesus in the Jesus myth.]
3.2.16. Philosophy: The Origins of
Man and Religion [Book Report: From Christianity Before Christ,
by John G. Jackson: The Pygmies of Central Africa are the descendants
of the Anthropoid Ape and thus the earliest man; in the Pygmy culture
we find the origins of man and religion; in the Pygmy mythology we find
an Adam story, a Father-God, a Virgin Mother whose Son was a Savior-God
who died for the salvation of mankind, was buried, resurrected, and
ascended into heaven; therefore, in the mythology of the Pygmies we
find the origins of Christianity.]
3.2.17. Philosophy: The
Christian Bible Old Testament and New Testament Sanction Slavery and
the Selling of Daughters To Be Maidservants [Is slavery and the
selling of daughters to be maidservants and therefore slaves okay in
the Christian Bible? The Old Testament (OT) Pentateuch--the first five
books of the OT and the basis of Jewish and Christian law--sanctions
both slavery and the selling of daughters to be maidservants. The New
Testament (NT) asserts that Jesus stated that he came not to destroy
the law but to fulfill it. By fulfilling the law/not destroying it and
thus not refuting the sanctioning of slavery and the selling of
daughters to be maidservants Jesus effectively sanctioned slavery and
the selling of daughters to be maidservants.]
3.2.18. Philosophy: Human
Sacrifice in the Christian Bible [Is human sacrifice sanctioned in
the Christian Bible Old Testament? Was not the execution of Jesus a
sacrifice in the Christian Bible New Testament?]
3.2.19. Philosophy: Is Genesis An
Original Jewish Scripture? [Is the Jewish/Christian Book of Genesis
in the Bible inspired by gods {Elohim} and therefore an original Jewish
work or is it a copy of earlier myths and thereby a man-made forgery?]
3.2.20. Philosophy: Does the
Christian Bible God Not Value Unborn Fetuses and Newborns?
[Biblical passages supposedly inspired by or otherwise direct quotes
from the Christian God clearly show that this God imposes
no value to unborn fetuses and newborn children.]
3.2.21. Philosophy: Pascal's Wager and
the Odds of Guessing Right [Pascal's Wager is between the choice of
belief in the existence of gods and nonbelief in the existence of
gods, and the claim of believers is that belief is the safer bet,
because if there is life after death then the believer stands to win
eternal happiness but the nonbeliever stands to lose eternal happiness
and gain eternal torment; if (A) there are seven major world religions
[Huston Smith: The Religions of Man], (B) one and only one of
these religions is the one-and-only true religion, and (C) guessing the
right religion will gain you eternal happiness and guessing the wrong
religion will gain you eternal torment, what are the odds of guessing
which is the right/true/one-and-only religion?]
3.2.22. Philosophy: What Was the
Sequence of the Execution of Jesus? [The Gospels of Matthew, Mark,
Luke, and John in the New Testament of the Christian Bible describe one
sequence for the execution of Jesus--by crucifixion--while the book of
Acts describes a different sequence for the execution of Jesus--by
unspecified execution then by being hanged upon a tree; since both
descriptions cannot be true,
herein is a serious biblical contradiction.]
3.2.23. Philosophy: Religious
Morality vs. Natural Morality: Which Is More Effective in Preventing
Crime and/or Immoral Behavior? A Survey of US Prison Inmates [Are
religionists more moral than nonreligionists including atheists and
agnostics? Can statistics re: the religious affiliation of US prison
inmates provide an answer?]
3.2.24. Philosophy: Is Islam a
Peaceful or Violent Religion? [Verses in the Koran, the holy book
of Islam, direct Muslims to actions which can be interpreted as
violent, including the killing and maiming of infidels, those who do
not
believe in Allah, Islam, Mohammed as a Messenger from Allah, or the
Koran, and including the subordination and beating of women.]
3.2.25. Philosophy: Evidence of
the Deism of the US Founders [Were the US Founders, the men who
created the US Constitution in the US Constitutional Convention,
Christians, and, thus did they intend that the US was to be founded on
Christian principles? Or were the Founders Deists, who, because of
their awareness of the Christian abuses such as the Inquisition which
were forced up innocent people when Christians were allied with or
otherwise in control of European governments, distrusted Christians,
and who therefore intended to found the US on Deistic principles to
ensure that Christians could not gain control of the US government?]
3.2.26. Philosophy: Christians and
Public Prayer/Worship [Freedom of religion ought to mean freedom
from religion. Out of common courtesy, Christians ought not to inflict
their religion upon others who do not share their religion and their
religious views. In the Book of St. Matthew in the Christian Bible, the
Christian mangod/godman, Jesus, strictly forbids Christians from
praying in public, from practicing their religion in public, and
instructs them to pray in private, and to practice their religion in
private.]
3.2.27. Philosophy: The Fundamental
Problem of Religion [Religion is a philosophy which includes a
belief in the existence of gods--supernatural or mystical beings; the
fundamental problem of religion is proving that gods exist.]
3.2.28. Philosophy: The Theology of
Christianity [The Old Testament of the Christian Bible, the
Christian holy book, teaches that man is a sinner, a
piece of crap in need of salvation from his sins by a dying/rising
savior-god, and the New Testament teaches that the one-and-only true
dying/rising savior-god is Jesus; Christianity rises and falls by the
belief that humans are sinners/pieces of crap in need of salvation by a
dying/rising savior-god named Jesus; if humans are not sinners/pieces
of crap, then a dying/rising savior-god is not needed, therefore the
dying/rising savior-god named Jesus is not needed.]
3.2.29. Philosophy: Is the US
Founded upon Christian Principles? [Christians claim that the US
was founded by Christians upon Christian principles which have Biblical
sources. What are the principles Christians claim are unique Christian
principles used by the Founders to found the US?]
3.2.30. Philosophy: Christianity and
the Bible on Abortion [Is abortion listed as a sin or a capital
crime in the Bible?]
3.2.31. Philosophy: Public Prayer
Is Public Practice of Religion and Forbidden by the US Constitution
[Commentary on a quote from Samuel Thompson]
3.2.32. Philosophy: Does Public
Practice of Religion Injure Innocent Individuals? [If freedom of
religion is implied in the US Constitution 1st Amendment, then so also
is implied freedom from religion. Freedoms--liberties--include both
freedoms of and freedoms from, and one of the freedoms
from is freedom from religion. When an individual's freedom from
religion is violated, infringed, then his liberty is infringed, and he
suffers therefore an injury.]
3.2.33. Philosophy: The US
Constitution and the US Treaty
of Tripoli Prove The US Was Not Founded upon the Christian Religion or
upon Christian Principles [US Const. Art. VI Sect 2 requires the
wordings of treaties to be included in US Law; The US Treaty of Tripoli
Art.
11 states the US Government was not founded on the Christian religion,
therefore the US Government is required to deny the US/US Government
was founded on the Christian religion.]
3.2.34. Philosophy: The Essence
of Buddhism: The Four Noble Truths [When Buddhism is stripped of
its three major mystical elements common to Eastern religions,
Samsara—The Wheel of Birth and Rebirth, Karma—What Works Are Done and
What Is Learned in This Life Accumulates and Applies inre One's
Station/Position in the Next Life, Nirvana—The Release from Samsara,
the philosophy that remains is based upon The Four Noble Truths—The
Essence of Pure Buddhism.]
3.2.35. Philosophy: Buddhism as a
Cognitive Psychology [Pure Buddhism, stripped of its Eastern
mysticism, deals with thinking and thinking disorders and thereby
qualifies as a cognitive psychology, probably the world's first and
therefore oldest cognitive psychology.]
3.2.25. Philosophy: The
Bible Is Not A Reliable Source of Information Inre God or the gods
[The Bible contains contradictions (multiple stories about the same
people, objects and events but with conflicting details), historical
inaccuracies, scientific inaccuracies, parallels (similar if not
identical people, objects and events to those found in other
religions/mythologies), and fictions (prophecies that either did not
predict the future or otherwise were not relevant to the people,
objects and event to which they were supposed to be relevant) that
reasonable humans have a right to expect would not be found in
so-called holy books thaat supposedly were written by or supervised by
God (Yahweh)/the gods (Elohim)]
3.2.26. Philosophy: Evolution vs
Creationism [The Bible is not a reliable source of information inre
God (Yahweh) or the gods (Elohim) and is therefore not a source of
information inre creationism but evolution has physical evidence that
serves as proof that evolution has occurred once life began on the
Earth. Evolution makes no claims inre abiogenesis
or the formation of life from non-life; instead, evolution describes
the fact that both macroevolution and microevolution have occurred in
the past, are occurring in the present, and are expected to occur in
the future.]
3.2.26. The Conceptualization of the Universe [Universe = All Reality; To conceptualize is to observe space, time, matter-energy, people, objects, and events and create concepts as mental representations – ideas, intuitions and names – inre the space, time and matter-energy that comprise the universe and the people, objects and events who/which exist in space, endure over time and are comprised of matter-energy and as causes cause as effects (A) changes of the physical states of pre-existing people, objects and/or events or (B) new people, objects and/or events from pre-existing matter-energy, principles as mental representations of the causalities and concidentialities between and among people, objects and events, and techniques as the application of principles for solving problems.]
3.2.27. Philosophy: Facts and Conclusions Inre The Universe and Gods [When the conceptualization of the universe is accurate and therefore is a fact, then the obvious conclusion inre gods is that they cannot and therefore do not exist beyond or outside or in addition to the universe and therefore the great gods of holy books including the Bible and the Koran who supposedly created the universe never existed but lesser gods as beings having greater knowledge than mankind of causality and coincidentiality and greater capabilities than mankind for causing effects currently cannot cause might exist and therefore be realities.]
3.2.28. What Is Religion? [Religion is a philosophy that includes a belief in the existence of gods. A definition of religion that insists a religion is a set of beliefs applies too broadly to too many sets of beliefs that can better/best be defined as philosophies. But that requires defining what is a philosophy, what is physics, and what is psychology, and what are gods, and specifying if/not gods exist. Summary: A religion is a philosophy that includes a belief in the existence of gods.]
4. Politics
Return to Page Links
Many
thanks to those who supported me and who voted for me in the NH 2002
Republican Gubernatorial Primary Election. The results showed a
surprisingly close election: Craig Benson won by only 55,000 votes! The
political solutions to political issues I presented are still valid and
need to be publicized and enacted and implemented. You can help by
sending letter-to-the-editors championing the political solutions you
favor, and you can lobby your state and federal representatives and
senators to accept and to act upon the political solutions you favor.
Again, many thanks for your support.
4. Political Science:
Bob K.
Political Stuff [A
political philosophy and vision for New Hampshire.]
I was a 2002 New Hampshire Republican
Gubernatorial Primary Candidate.
On this link are political thoughts for New Hampshire in 2002.
NOTE: This article is being updated continuously. Check frequently
for updates.
Letters-to-the-Editors: If you find ideas you like, you
can help by writing letters-to-editors.
Please see Dan Mason's stunning Letter-to-the-Editors: Dan Mason's Letter of Support, The Union
Leader, 8/28/02, P. A13.
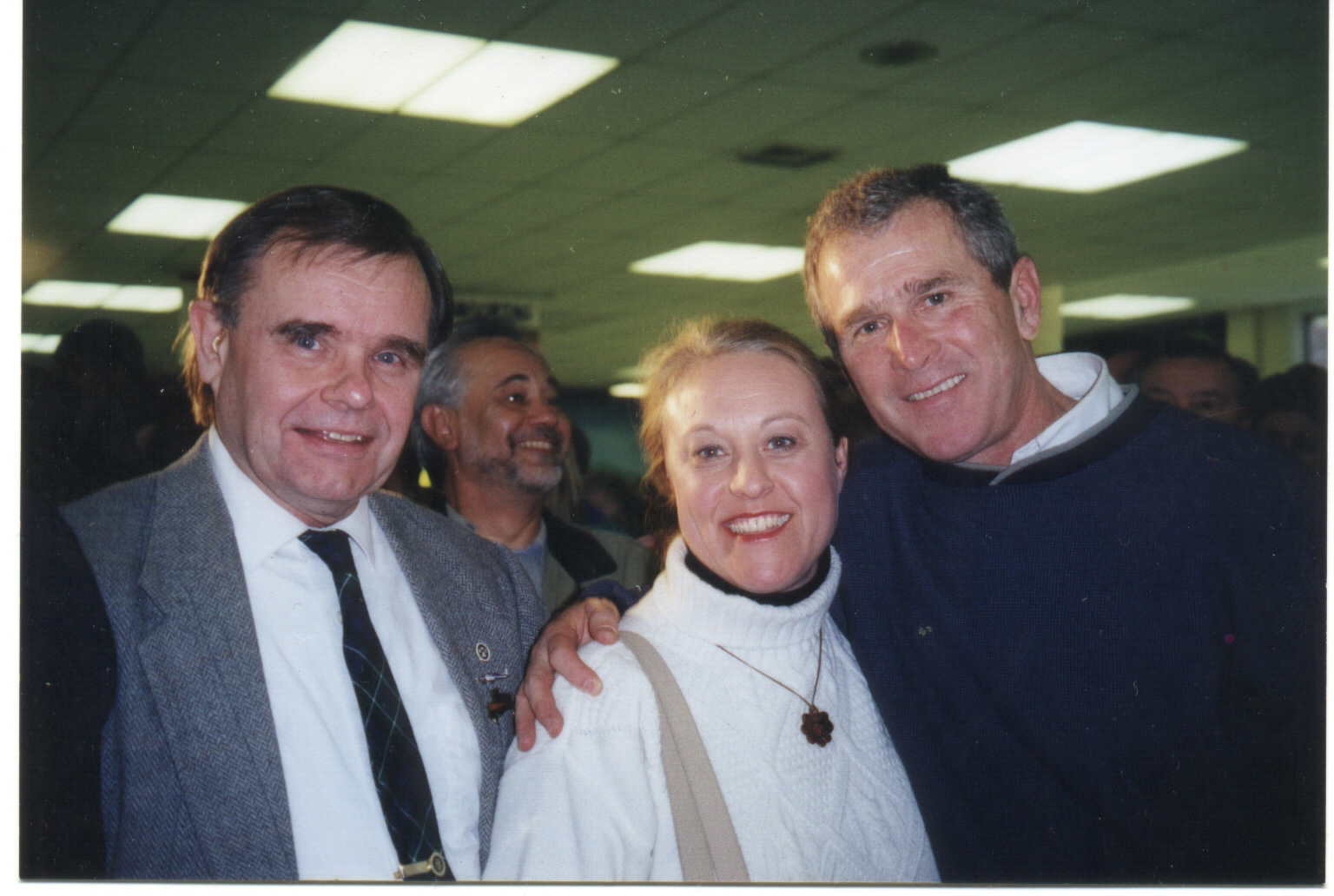

Bob and Janice Kroepel with George W. Bush,
Alvirne High School, Hudson, New Hampshire,
during the Presidential Primary Campaign of 2000.
Bob K. Political Priorities
Statement of Political Purpose
Campaign Song: "I'm Coming Home
To You, New Hampshire"
Citizen Petition Initiatives
and Legislative Referendums
Education Funding
Education Reforms
Medical Care Reforms
Pro Gun: Pro Second Amendment
Abortion
School Prayer
Personal Termination/Assisted
Suicide
State Control of Wholesale
Prices
Ineffective Laws That Injure
Innocent People
Standards for Public Laws and
Policies
Standards for ESCR Need and
Morality
Why I Am a Republican and Not
a Democrat
The World's Longest Humorous
Political Slogan/Bumper Sticker
What's In A Name: Kroepel?
Why I Am A Moderate Republican
Political Qualifications:
Experience; Accomplishments
Bob K. Bio
Selfish Reasons for Wanting To
Be Governor of NH
Dan Mason's Letter of Support, The
Union Leader, 8/28/02, P. A13
Was The US Founded as a
Christian Nation? Or as a Deistic Nation?
The Classification of Life
Forms: The Implications for the
Abortion Political Issue
Abortion = Justifiable
Homicide
Cleisthenes, The Developer of
Democracy
INRE Abortion: The True Facts
of Human Life
ESCR (Embryonic Stem Cell Research)
vs ASCR (Adult Stem Cell Research)
The
Common Creed (Of All People)
The Duck Theory
Applied to Democrats
Democrat Party America
(DPA) Policies vs Communist Party America (CPA) Policies
Democrats and Communism
The Essence of the Law
The American Language
Governor Bradford's Journal:
History of Plymouth Plantation: Private vs Communal Farming
The Purpose of the US Constitution 2nd Amendment
(HTM Webpage Version) The Purpose of the US Constitution 2nd Amendment
Return to Page Links
Campaign Song
I'm Coming Home To You, New Hampshire
Robert Howard Kroepel
Copyright © 2000
Chorus: I'm coming home to you, New Hampshire.
I'm coming home, where the air is clear.
I'm coming home to see your face once more.
Please open wide your welcome door.
Verse 1: In the spring I love your lilacs,
In the summer, your sea and lakes,
In the fall, the autumn wonder,
And the snow that winter makes.
Chorus: I'm coming home to you, New Hampshire.
I'm coming home, where the air is clear.
I'm coming home to see your face once more.
Please open wide your welcome door.
Verse 2: Most of all I love your people.
I love their smiles and the way they care.
I want to see my friends and fam'ly,
And find the love I need to share.
Chorus: I'm coming home to you, New Hampshire.
I'm coming home, where the air is clear.
I'm coming home to see your face once more.
Please open wide your welcome door.

***A live performance of I'm Coming Home To You, New Hampshire
can be found in the MP3 files section: http://www.bobkwebsite.com/ImCmngHomeToYouNH1.mp3
5. Personal and
Business Consulting
Return to Page Links
5.1.
Consulting:
Personal Problem-Solving [Self-help seminars based
upon Operational Psychology] [Not Yet Available]
5.2. Consulting:
How to Think Straight [Thoughts on
straight thinking; includes Operational Psychology; available as an
unfinished manuscript in 8.5 in. x 11 in. comb binding format]
6. Physics
6.1.
Operational Physics
Return to Page Links
6.1.3. Physics:
The
Theory of Invariable Time-Intervals [TITI] [The essence of time
measurement is the time-interval. Einstein developed the Special and
General Theories of Relativity using as one of his premises variable
time-intervals as found in clocks which are affected by changes of
velocity and/or gravity. What happens to Special and General Theories
of Relativity when Einstein's variable time-interval premise is
replaced by a premise which features invariable time-intervals as found in
clocks which are motion-sensing and gravity-sensing and self-adjusting
to compensate for changes of velocity and/or gravity or in clocks which
are synchronized by radio signals from a master
clock?]
6.1.4. Physics:
Confirmation of the
Theory of Invariable Time-Intervals [One of the criteria for the
confirmation of the Theory of Invariable Time-Intervals (TITI) would be
the actual existence and practical usage of invariable time-interval
clocks (ITICs). ITICs have been found to be used for the GPS (Global
Positioning System), thus confirming the TITI.]
6.1.5. Physics:
Can Physicists Detect
Absolute Motion (AM), Absolute Rest (AR), and/or the Absolute Rest
Reference Frame (ARRF)? [In theory, a definition of time can be
used to detect AM/AR/the ARRF.]
6.1.6. Operational Physics:
Operational Physics
[The Concepts and Principles of Operational Physics]
6.1.7. Operational Physics:
The
Einstein Railway System and the Speed of Light and the Determination of
Simultaneity [Einstein's original diagram of his
railways system consisting of a railway embankment with observer M and
a railway carriage with observer M' and newer diagrams of the Einstein
Railway System relevant to the speed of light and the determination of
simultaneity.]
6.1.8. Operational Physics:
The Heisenberg Uncertainty
Principle/HUP [Do causality and therefore determinism occur at QM
scalar levels? Yes, they do!]
6.1.9. Operational Physics:
Simultaneity
[What is
simultaneity? What
is Einstein's conception/principle of
simultaneity?
What is the modern definition of
simultaneity?
What is the relationship, if any, between
simultaneity and the speed of
light? What are the modern criteria for the determination of
simultaneity?]
6.1.10. Operational Physics:
Time &
Simultaneity & The Arrow of Time [The 2008 Operational Physics
concepts and principles inre Time.]
6.1.11. Operational Physics:
The Spaceship
and RC Diagrams and DVs [The Spaceship Diagrams and DVs and the RC
DVs.]
6.1.12. Operational Physics:
The K and K'
Diagrams [Diagrams of the changes of the lengths of rulers and the
rates of ticking of clocks which are accelerated from an initial
reference frame K to a new reference frame K'; clicking the link will
open a PDF file with the relevant text and diagrams.]
6.1.13. Operational Physics:
The Orbiting
Stars Diagrams and Movies [Diagrams—which are graphs—and iMovies
which illustrate (1) the fact that light has an absolute velocity (AV)
of 186, 000
mps, i.e. AV = 186,000 mps, relative to the spacepoints at which light
is emitted from lightsources, (2) the fact that the motion (velocity)
of a lightsource does not affect the motion of light, (3) the fact that
the spacepoints at which light is emitted from
lightsources have no motion and are therefore at-rest at AV = 0 mps,
(4) the fact that all lightrays moving at AV = 186,000 mps in the
same direction of motion have the same relative velocity (RV) and that
RV = 0 mps, (5) the fact that lightrays which have an AV = 186,000 mps
relative
to their emission spacepoints and an RV = 0 mps relative to each other
are all in the same reference frame—the reference frame of light—the
light reference frame (LRF), and (6) the fact that the emission
spacepoints are at-rest/not-in-motion
and therefore all emission spacepoints have an AV = 0 mps which is also
an RV = 0 mps which means that all emission spacepoints are at absolute
rest (AR) in the same reference frame, the absolute rest reference
frame (ARRF).]
6.1.14. Operational Physics:
The Einstein
Railroad Diagrams [Diagrams and iMovies which, using adaptations of
Einstein's Railroad Drawing from
Relativity,
1961 edition, illustrate the Twin Light Motion Facts, TLMFs, which are
(1) light travels at an AV = c or 186,000 mps relative to the
spacepoint at which it was emitted and (2) the motion of a lightsource
does NOT affect the motion of light which are fundamental to the
objective truth/reality inre the motion of light, and the fact that the
motion of light for Einstein's conception of simultaneity has to be an
absolute velocity, AV, of c relative to the spacepoints
at which lightpulses were emitted from their lightsources and NOT
relative to the lightsources, and, therefore, the motion of light past
Einstein's Train has to be and therefore is a relative
velocity, RV, which, depending on direction of motion, but assuming
that the lightpulses are in motion parallel to the motion of the Train,
has to be RV = ± c instead of AV =
c, which means the speed of light is NOT the same for any and all
observers in any and all reference frames, a refutation of one of
Einstein's postulates for special relativity.]
6.1.15 Operational Physics (2011):
The Law of
Physical States and The Corollaries of the Law of Physical States.
[The Law of Physical States replaces The Law of Inertia and The
Corollaries of The Law of Physical States replaces The Corollaries of
the Law of Inertia. A physical state includes any and all
observable/measurable characteristics of an entity, a person or object
which/which is comprised of matter/energy (m/e), including size, shape,
mass (weight), color, m/e composition, oscillation (rate
of ticking for clocks), motion (inertial state: being at-rest or
in-motion), location in space (position), timepoint (time mark on a
continuum of time), duration (age, endurance), etc. The Law of Physical
States and The Corollaries of The Law of Physical States describe
causality as forces, which are forms of m/e, as causes causing as
effects (A) changes in the physical states of entities or (B) new
entities from pre-existing m/e and determinism as causes determining
effects, effects are determined by causes, etc.]
6.1.16 Operational Physics (2011):
Speculations 1.
[Speculations/Brainstormings inre simultaneity, timepoints, the
universal m/e
configuration, the continuum of universal time, 3D holograms,
causality, causal relationship v coincidental relationship,
determinism, causality/determinism sequence, If P, Then Q logical
arguments, temporal measurement not causal, spatial measurement not
causal, time not a causal component of spacetime, space not a causal
component of spacetime, therefore spacetime is not comprised of space
or time, and, therefore, spacetime can only be comprised of m/e, which
is causal.]
6.1.17 Operational Physics (2011):
Speculations
2. [Absolute simultaneity, the occurrences of events on different
reference
bodies at the same timepoint, would require absolute time clocks (ATCs,
ITICs, non-distortable clocks) which are "independent of the state of
motion of [their bodies] of reference" [Einstein, Relativity, 1961
edition, p. 27] for the identical timepoint needed for determining
absolute simultaneity.]
6.1.18 Operational Physics (2011):
Speculations
3. [The Operational Physics (OpPhys) Theory of Time, distortable v
non-distortable/adjustable rulers and clocks, the text-only
illustrations (Figs 1 and 2) of the Theory of the Spacegrid using only
those characters available on a typical computer keyboard, the relative
velocity (RV), measured velocity (MV), The Law of Physical States and
The Corollaries of the Law of Physical States (earlier versions), The
Extrapolation Theory.]
6.1.19 Operational Physics (2012)
The Einstein Light Motion
Paradox. [Inre
Relativity,
1961 edition, Chapter IX, Einstein's Fig. 1 Railroad Drawing,
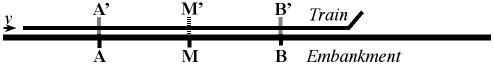
Fig. 1 (Redrawn),
suggests that light travels at a relative velocity (RV) of 1.00c or
186,000 mps relative to the Embankment but an an RV ≠ 1.00c relative to
the Train; this intuition conflicts with the relativistic axiom that
light travels at RV = 1.00c inre all observers regardless of their
reference frames/bodies, and, thus, there is the Einstein Light Motion
Paradox inre the motion of light inre the Embankment and the Train inre
Fig. 1; the Michelson-Morley Interferometer Experiment (MMIX) Result 2:
The speed of light is the same for all observers is thus false.]
6.1.20 Operational Physics (2012):
Timepiece
Timerates and Absolute Velocity (AV). [The timerates of timepieces
(clocks, watches, etc., used to measure time) can be used to determine
if or not a condition of absolute velocity (AV) of 0.00c (absolute
rest, AR) is a reality, e.g. AV = 0.00c.]
6.1.21 Operational Physics (2012):
The Link between
Time and the Universal Matter-Energy System [There is a link
between time and the universal matter-energy (m/e)
configuration that reveals the sequences of events, the simultaneities
of events, the causalities of events, and the changerates (rates of
change) of events.]
6.1.22 Operational Physics (2012):
Converting
The Law of Inertia to The Law of Causality [The Law of Inertia can
be converted to The Law of Causality.]
6.1.23. Operational Physics (2012):
The
Operational Definition of Time [The 2012 Operational Physics
operational definition of time.]
6.1.24. Operational Physics (2020):
The Motion of Light [The description of the motion of light inre passing the centers of mass (CoMs) of entities (objects, things).]
6.2.
General Physics
Return to Page Links
6.2.1. Operational Physics:
The
Law of Inertia and Its Corollaries [What is the Law of Inertia? Is
it the fundamental law of physics? What are the Corollaries of the Law
of Inertia?]
6.2.2. Physics:
A Concept of
the Universe: Three Realities, Three Infinities, and One Finity
[The universe consists of three realities--(1) the spatial reality:
space, (2) the temporal reality: time, and (3) the physical reality:
matter and energy, and their infinities--the unbounded and limitless
space, the never-begun and never-ending continuum of time, and the
indestructibility of matter/energy, and the finity of matter/energy:
the finite
quantity of matter/energy.]
6.2.3. Physics:
The Theory of
the Practical Limits of the Inverse Square Law [In theory, there is
no limit to the ranges of force fields, such as gravitational fields as
described by the inverse square law wherein the strength of a field is
inversely proportional to the distance from the field source, or
sources; but in practical reality there is a point which is a limit to
the field range wherein the force of or in a force field is so weak it
cannot cause observable and therefore measurable effects upon physical
phenomena, upon matter/energy, and, therefore, there is a practical
limit to the range of force fields, including gravitational and
electromagnetic fields.]
6.2.4. Physics:
The Theory of the
Perfect Observer [Quantum Mechanics, QM, says we cannot observe and
not disturb small stuff, and, therefore, we cannot determine both
the velocity and position of individual small stuffs, and, therefore,
we cannot determine causality among small stuffs and, therefore, we
cannot make deterministic predictions of individual small stuffs, and,
therefore, we have to make probibalistic predictions instead of
deterministic predictions. What if we were Perfect Observers, able to
to observe and not disturb, and, therefore, be able to determine
determinism, properly called causality, at the level of individual
small stuffs?]
6.2.5. Physics:
The Who?
What? Where? When? and Why? of Physics
[Who?/What?/Where?/When?/Why? are the people/things/events in physics
who/which are the answers to the questions of
Who?/What?/Where?/When?/Why? in physics?]
6.2.6. Physics:
The Theory of Theories
[What is a theory? An hypothesis/prediction to be proved? Or a proven
description of causality? An explanation?]
6.2.7. Physics:
The
Extrapolation Principle[Causalities between/among
people/objects/events observed on small scales can be assumed to occur
at all other smaller and larger scales until disconfirming/falsifying
people/objects/events are observed.]
6.2.8. Physics:
Universe = All
Reality = Space/Time/Physics (M/E) [Howitiz that the Universe is
comprised of Space, Time and Physics (Matter and Energy—M/E)]
6.2.9. Physics:
If P, Then
Q Logical Arguments and Causality
[If P, Then Q logical arguments are descriptions and predictions of
causality—the sequence in which Ps which are conditions and causes
cause Qs which are consequences and effects.]
6.2.10. Physics:
Converting
The Law of Inertia to The Law of Causality [The Law of Inertia can
be converted to The Law of Causality.]
Return to Page Links
7.1. Science:
The Code of Science
[A Theory of Science and
the Code by which all scientists must abide.]
7.2. Science:
Operational Definitions
[Operational definitions are descriptions of observations and
measurements of people/things/events; Operational definitions enable
people to create concrete definitions of abstract terms; Operational
definitions are required by The Code of Science for effective
communication (A) among scientists and (B) among scientists and
nonscientists.]
7.3. Science:
The Classification
of Life Forms [What is life? Are there generic characteristics of
all life forms? Are there specific characteristics of some but not all
life forms? Can we therefore classify life forms as generic vs.
specific?]
7.4. Science: Philosophy:
The
Three Forms of Human Life [Human life forms evolved from early life
forms to early human life forms to human parents who produce human
gametes when when fertilized produce human zygotes.]
7.5. Science:
What Is Life? [What is
life? Do we have enough knowledge to be able to define what is life? A
theory of life.] [NOTE: This theory of life is being developed and
therefore will be revised – it is not claimed to be perfect nor complete
at this timepoint in history; it is, however, at least a start in
developing a perfect and therefore complete theory of life.]
7.6. Science:
When Does/Did Life
Begin? [When does life begin? When did life begin? Some proposals
for answers.]
7.7. Science:
The
Theory of Theories [What is a theory? An hypothesis/prediction to
be proved? Or a proven description of causality? An explanation?]
7.8. Science:
Mediocre
Minds [What are Great Minds v Mediocre Minds? How can mediocre
minds be identified?]
7.9. Science:
If P, Then Q
Logical Arguments and Causality
[If P, Then Q logical arguments are descriptions and predictions of
causality—the sequence in which Ps which are conditions and causes
cause Qs which are consequences and effects.]
7.10. Science:
Converting
The Law of Inertia to The Law of Causality [The Law of Inertia can
be converted to The Law of Causality.]
7.11. Science:
Evolution vs
Creationism
[The Bible is not a reliable source of information inre God (Yahweh) or
the gods (Elohim) and is therefore not a source of information inre
creationism but evolution has physical evidence that serves as proof
that evolution has occurred once life began on the Earth. Evolution
makes no claims inre
abiogenesis
or the formation of life from non-life; instead, evolution describes
the fact that both macroevolution and microevolution have occurred in
the past, are occurring in the present, and are expected to occur in
the future.]
8.
ProMUSE
(Professional Music/Entertainment)
Return to Page Links
8.1.
ProMUSE [Professional Music Services]
- I am one of New England's longtime professional musicians. I
have played the organ and the piano with the pedalbass in nightclubs
and restaurants, and for functions
including many weddings and private parties.
- I have had the pleasure of playing piano for President and Mrs.
George Herbert Walker Bush in Kennebunkport, Maine.
- If you need fine quality piano music for your restaurant, lounge
or
private function, contact me at
Home:
603-859-7873
Cell:
603-767-6021
Email:
kroepel@tds.net
8.2. ProMUSE: Standard Paragraph [Public Relations Press Release]:
Bob Kroepel, Professional Musician
8.3. ProMUSE: Bob K Flyer:
Bob K Flyer
8.4. ProMUSE: Bob K Songlist:
Bob K Pop Songlist
8.5. ProMUSE: Bob K Jazz Songlist:
Bob K Jazz
Songlist
8.6. Demo Song:
Bob
K Theme Song
[Live, Piano, Bob K Original Composition © 2006]
8.7. Demo Song:
I'm Coming
Home To You, New Hampshire [Live, Piano, Pedalbass (a set of
footpedals similar to spinet organ bass pedals, and used for playing
bass notes.
for the sound of Piano plus Bass), and Vocal (no effects on the vocal
track), Bob K Original Composition © 2002]
9. TeachMUSE (Teaching Music)
Return to Page Links
9.1. TeachMUSE [Music teaching services]
If you are searching for fine quality music lessons for yourself
or someone else, contact me at
Home: 603-859-7873
Cell: 603-767-6021
Email: kroepel@tds.net
I teach music lessons in students' homes in the
towns and cities of New Durham, Alton, Barnstead, Wolfeboro, Gilford,
Laconia, Milton, Middleton, Rochester, Somersworth, Barrington, Dover,
and Portsmouth in New
Hampshire.
Basic Music Theory [Recommendations
for teaching music theory for popular music and classical music.]
Because you would need music fonts to see sharp signs and flat signs
instead of # or b, and because music fonts are not to be shared without
compensating their creators, the necessary sharp and flat signs will be
the Times font "#" and "b".
Check out on the Mel Bay Publishing Company website, www.melbay.com, the Mel Bay Creative
Keyboards Webzine [magazines published upon websites] Creative Keyboards for my
articles: May, 2000: When The
Saints Go Marching In: An Introduction to Jazz Piano, and June,
2000: Creating
Ideas for Jazz Solos
9.2. What Is Jazz? [One of the hallmarks
of
jazz is the jazz solo, the improvisation, the spontaneous creation of
melodies over the original accompaniment rhythm pattern played by the
rhythm section of a band or by the pianist's left hand; but the true
hallmark of jazz is the jazz arrangement, the sequence of song parts
and arrangement ideas jazz musicians typically use when they play a
jazz
version of a song.]
9.3. The Vocalist's Profile [A
listing of the vocalist's vocal range, a description of Basic
Philosophy (Operational Philosophy) and Basic Psychology (Operational
Psychology) to help a vocalist understand reality and human nature in
preparation for interpreting (imagining and emulating) the actions and
reactions of the personality in the lyrics of a song who is the
storyteller, and an operational definition of art by a description of the people
(characters), objects (physical realities) and events (plot) who/which
in art are artificial and the
people (artists, producers, directors, crew members, etc.), objects
(props, cameras, sound stuffs, stage stuffs, etc.) and events in art who/which are real(ity), and
the vocalist's repertoire (list of songs which are presentable to an
audience).]
Return to Page Links
10.
General
Music (Music Services, Sheet Music Services, Etc.)
Return to Page Links
11.
Music Schedule 2018
Return to Page Links
Friday & Saturday Nights: Tavern 27, Laconia NH: 8-10 PM: Piano: Classic Pop Music: Music Menu and Text Requests.
Sunday Mornings: Chocorua Community Church, Tamworth, NH: 10-11 AM: Organ and Piano: Sacred, Spiritual and Gospel Music.
Sunday Afternoons: Hobbs Tavern, West Ossipee, NH: 12-3 PM: Piano: Classic Pop Music: Music Menu and Text Requests.
Return to Page Links